Eye on electricity
Snowmelt: a seasonal boost to hydro lake levels
Why is snowmelt vital to the generation of New Zealand's electricity? What does it mean for hydro electric power?
- Generation
- Low emissions
In New Zealand, between 80-95% of electricity is generated by renewable sources, with the majority produced by hydro dams. Most dams are in the South Island and their electricity is ferried to the North Island via large cables (called the High-Voltage Direct Current or HVDC).
The additional water used in dams (hydro storage) is refilled by both rain and snow, with snow having a particularly strong seasonal impact on storage. Hydro lake levels typically drop during autumn and winter, as hydro generation runs hard and rain falls as snow on the slopes of the Southern Alps. Then snowmelt flows into the hydro lakes in spring and summer. This snowmelt contributes to between 20-70% of spring and summer water inflows1 in the South Island’s hydro lakes.
There are three main water catchments in the Southern Alps, the:
- Waitaki river, which feeds hydro dams like Benmore and Aviemore;
- Clutha river, which runs through the Clyde and Roxburgh dams; and
- Waiau river, which flows through the Manapōuri Power Station.
Snow typically accumulates at elevations above 1,000 metres, so the first two catchments experience more snowmelt as their mountains are higher.
New Zealand experienced its wettest winter on record in 2022. In late October 2022, national hydro storage was 23% percent above the historic mean ie, the lakes were high, when typically, they would be low. Hence, snowmelt - combined with already high lake levels - could see high hydro storage persist at lakes Pūkaki, Hawea and Takapō throughout the remainder of the year2.
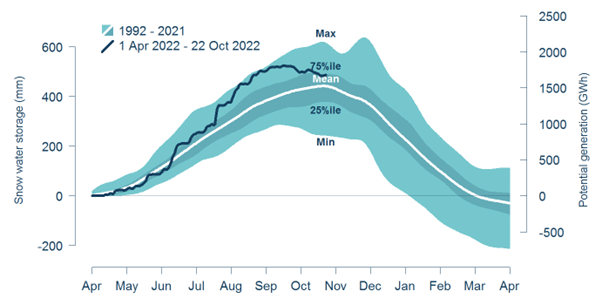
Figure 1 shows an estimate of snow storage in the Waitaki catchment up to 22 October 2022, produced by Meridian Energy. Meridian estimate that the Waitaki catchment has ~1,500 GWh of snowmelt in the catchment on 22 October 2022, which is above the 75th percentile. Lakes with less snowmelt, however, like Manapōuri and Te Anau, could remain with low hydro storage, especially as NIWA are forecasting normal or below normal rainfall3.
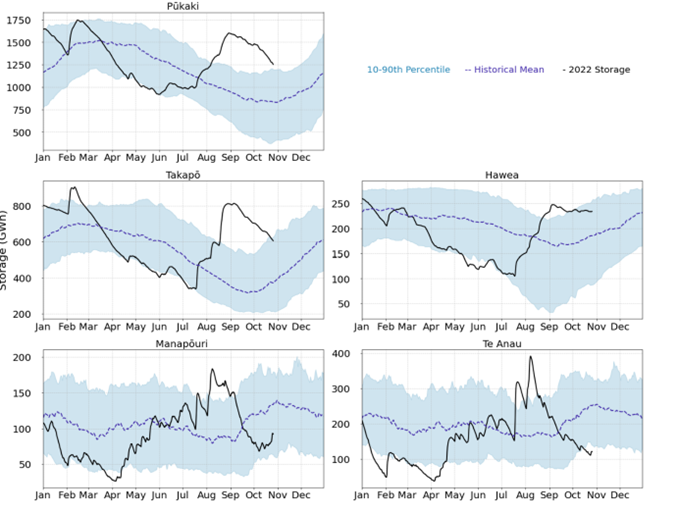
Figure 2 shows storage at New Zealand’s main hydro storage lakes in 2022, alongside the historic mean and 10th and 90th percentiles of lake levels.
Snowmelt is vital to New Zealand’s electricity generation. Ongoing work seeks to improve our understanding. This online tool visualises where precipitation anywhere in the world will flow. For example, see this example of a raindrop (or snow flake) falling in the Southern Alps, and how this snow fall eventually runs out along the Clutha river through the Clyde and Roxburgh power generation dams. The NIWA website also displays snow depth across different mountains in New Zealand.
The Electricity Authority monitors hydro storage and how it changes throughout the year. See current and past national hydro storage levels.
Related News
Deadline extended for non-discrimination obligations consultation
On 26 February, the Energy Competition Task Force launched a consultation on certain aspects of the proposed non-discrimination obligations, which are aimed at…
Policy changes to strengthen dry year risk management
The Electricity Authority Te Mana Hiko has approved changes to the Security of Supply Forecasting and Information Policy to improve certainty and better suppor…
Electricity Authority launches new consultation on non-discrimination obligations
The Electricity Authority Te Mana Hiko has launched a further consultation on certain aspects of the proposed non-discrimination obligations, which are aimed a…
